If you’ve had even a little bit of exposure to the world of cars you’ve probably heard of a turbo or turbocharger before. But just what is a twin turbo?
A twin-turbo engine is simply an engine with two turbochargers instead of just one or none at all. These twin turbochargers help get more air into the engine, which increases the amount of horsepower produced.
While most normal cars don’t have a twin-turbo setup, single turbochargers are appearing more and more commonly in the engines of average everyday vehicles, and knowing a bit more about these different engine configurations can make you a more informed car owner and allow you to make better decisions if you are planning on buying a car in the near future.
What Is A Turbocharger?
A turbocharger is a part that can be installed in an engine that helps force more air into the engine in order to increase its power output. Basically, adding a turbocharger to an engine that doesn’t have one will increase the amount of power that you’ll be able to get out of it.
One of the main benefits of turbochargers is that they are powered by the exhaust gas that your engine expels as it runs. This means that your engine doesn’t have to waste too much extra fuel to get that added boost of power, instead being powered by gases that would otherwise go to waste.
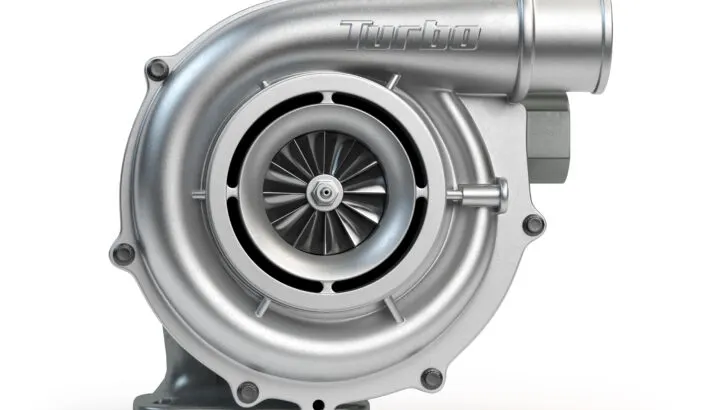
Turbochargers essentially consist of three main components: the turbine, the compressor, and the center housing hub rotating assembly, which houses and connects the two.
As your engine expels exhaust, the exhaust gases spin the turbocharger’s turbine, which in turn powers the compressor. The compressor then sucks in outside air through the engine’s intake system, compresses it to the right pressure, and then feeds it into the engine’s combustion chambers.
When your engine’s engine control unit notices the increased amount of air being sent into the engine, it sends an equally increased amount of fuel into the combustion chambers with it. This makes a larger explosion in the combustion chamber that creates a lot more power than the engine normally would with a less dense mixture of fuel and air.
However, the turbocharger isn’t on all the time. In fact, the turbocharger only activates when the engine achieves a certain engine speed. This means the harder you push down on the gas pedal, the harder the turbo will work, while at lower speeds it may not kick in at all.
Turbochargers are becoming more and more common in average everyday vehicles. Turbocharging a small 4-cylinder engine can provide the extra power it might need to easily overtake other vehicles at highway speeds while still providing impressive fuel economy when driving normally.
In short, turbocharging an engine can allow a smaller engine to produce a similar amount of power to an engine with a larger displacement, while still maintaining impressive fuel economy during everyday driving.
What Is Turbo Lag?
While so far it may seem like there are only benefits and no drawbacks to turbocharging an engine, there is one big drawback.
Basically, turbo lag is the amount of time it takes for the turbo to provide that extra boost after you press down on the gas pedal. As stated above, turbochargers aren’t on all the time and only start working when the engine speed reaches a certain rpm, so there is always some sort of delay between the time when you press down on the gas and feel that extra boost.
This delay exists because turbochargers are powered by exhaust gas and it takes time for the engine to build up sufficient exhaust pressure to spin the turbine and power the compressor that forces the extra air into the engine.
What Is a Twin Turbo?
As the name suggests, a twin turbo is simply any engine that uses two turbochargers instead of one. The benefits of a twin-turbo setup vary depending on how you configure them, but no matter what the configuration is, having two turbos instead of one will allow your engine to intake even more air and produce even more power.
There are three main types of twin-turbo configurations including parallel, sequential, and serial configurations.
Parallel Configuration
The most common setup is a parallel configuration. Particularly useful for V-shaped engines like a V6 or V8, this configuration sets the two turbochargers parallel to each other with one on each side of the V.
This allows each turbocharger to can start spinning more quickly and more directly feeding air into the combustion chambers, instead of having one turbocharger that has to push air through all sorts of complicated piping to reach every cylinder.
This can help reduce turbo lag, especially if you use two smaller turbochargers that will allow them to start spinning at lower RPMs than a larger single turbo would.
Sequential Turbocharging
Sequential turbocharging is great for taking care of pretty much every disadvantage to having a single turbocharged engine. It works by using two different-sized turbochargers that work together to provide extra power at all engine speeds.
At low engine speeds, the engine is able to primarily send gas to the smaller turbocharger producing extra power at the lower end. Then, as you press farther down on the gas pedal and RPMs increase, the exhaust will get directed to the larger turbo, which continues to provide extra power on the high end, virtually eliminating turbo lag altogether.
Serial Turbocharging
In serial turbocharging, instead of having the turbos work separately – either at different RPMs or on different banks of cylinders – they are set up in a series with the compressed air from the first turbocharger being fed into the second for further compression.
This can provide a ton of power because so much additional air is sent into the engine at once. However, this can actually make the problem of turbo lag worse, especially at low RPMs.
Is a Twin Turbo Faster Than a Turbo?
While this mostly depends on what type of engine the turbos are attached to and the size of the turbochargers themselves, if you take two cars with the same engines and then turbocharge one of them and twin turbocharge the other, the twin-turbocharged engine will almost definitely be faster.
As we know, feeding a higher concentration of air and fuel into an engine’s combustion chambers will produce a more powerful explosion that provides more power to the vehicle. Adding that second turbo will provide double the amount of air to the engine and create significantly more power than one turbo will by itself.

A twin-turbo setup will also have less turbo lag at lower RPMs, meaning that that extra power will kick in quicker and at lower speeds giving the twin-turbocharged engine a huge advantage in acceleration over the single-turbo engine.
Twin Turbo vs. Supercharger
If you know what a turbocharger is, there’s a pretty good chance you at least have a general idea of what a supercharger is. We often associate turbochargers and superchargers with fast sports cars, but how are they different and which one is better?
A supercharger essentially does the same thing that a turbocharger does. It takes in air, compresses it, and sends the increased quantity of air to the engine, just like a turbo does. However, the big difference is that instead of being powered by the kinetic energy from expelled exhaust gases, it is directly powered by the engine.
The benefit of this is that there is no lag like there is with turbochargers. Since the supercharger is directly powered by the engine it is always running and doesn’t need to wait for exhaust pressure to build up before activating, allowing it to run constantly and respond to you pressing down on the gas pedal instantaneously.
The downside to this, however, is that superchargers tend to eat up more fuel than turbochargers do. Since the supercharger is directly powered by the engine, it requires extra gas to power the compressors, meaning that the engine will always consume more fuel than a similarly sized turbocharged engine would.
Because of this, while you could make the argument that a supercharged engine is better that an engine with a single turbocharger, a twin-turbo setup will almost always be superior due to the decreased amount of turbo lag and superior fuel economy.
Key Takeaways to a Twin Turbo
A turbocharger is a part of an engine that uses the kinetic energy from expelled exhaust gases to power a compressor that feeds an increased amount of air into an engine’s combustion chambers.
Turbo lag is the lag felt between the time that you press down on the gas pedal and when the turbo kicks in.
A twin-turbo engine is any engine with two turbochargers instead of one.
Twin turbo systems allow for increased power output over single turbo setups and reduce turbo lag.
Turbochargers and superchargers do the same thing, they are just powered differently.
